Addison's disease can be explained on the basis of a deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone
Common findings:
The most common cause of Cushing syndrome: iatrogenic, from administering exogenous steroids, such as prednisone.
The next most common cause is known as Cushing's disease, it results from increased adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion from pituitary, which causes increased adrenal production of cortisol.
Central Obesity with sparing of the limbs is characteristic of Cushing's syndrome. e.g. truncal fat with relatively thin limbs.
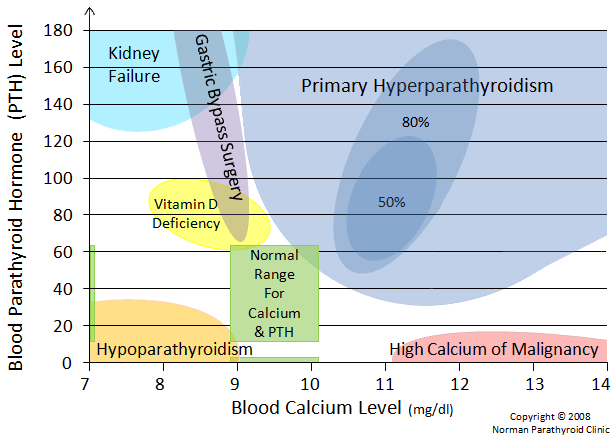
Great information on this page: http://www.parathyroid.com/hyperparathyroidism-dia..., including amazing diagrams like this one:

Desmopressin acetate (DDAVP)
This medication is used as the first-line treatment in patients with central or primary diabetes insipidus (DI). Arginine vasopressin (AVP), or antidiuretic hormone, is produced by the pituitary gland and works on the renal tubules within the kidney to concentrate the urine and reduce water loss. DI occurs when there is a deficiency in AVP, and these patients produce large amounts of dilute urine. As a result, patients can experience excessive thirst, polyuria, nocturia, headache, dehydration, and disturbances in vision. Central or primary DI can be diagnosed with 24-hour urine collection or vasopressin challenge test. Once the diagnosis is established, the first line treatment is usually desmopressin acetate, which is a synthetic form of AVP. It has a longer antidiuretic action than AVP and does not constrict smooth muscle. DDAVP is available in oral, nasal, and injectable preparations. While being treated, it is important to control fluid balance in order to prevent dehydration, monitor the patient's weight daily, and monitor electrolytes.
EM:RAP July 2017 Hyperglycemia but not DKA
ADA defines DKA as BG > 250 + ketosis (serum or urine) + metabolic acidosis